Why Are So Many Businesses Upgrading Oracle E-Business Suite to 19c?
Why Are So Many Businesses Upgrading Oracle E-Business Suite to 19c?
Since the Oracle E-Business Suite (EBS) upgrade to 19c was released, businesses have been busy upgrading their EBS databases. The latest upgrade provides a multi-tenant architecture that allows for database consolidation and data/metadata manageability.
The Figure 1 outlines the lifetime support policy and plan:
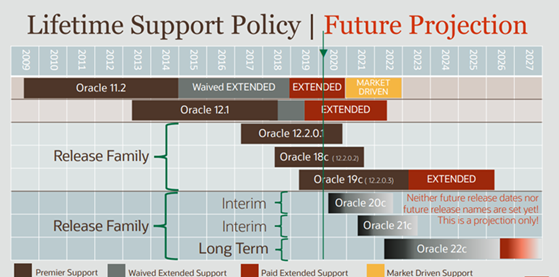
Figure 1: Lifetime Support Timeline
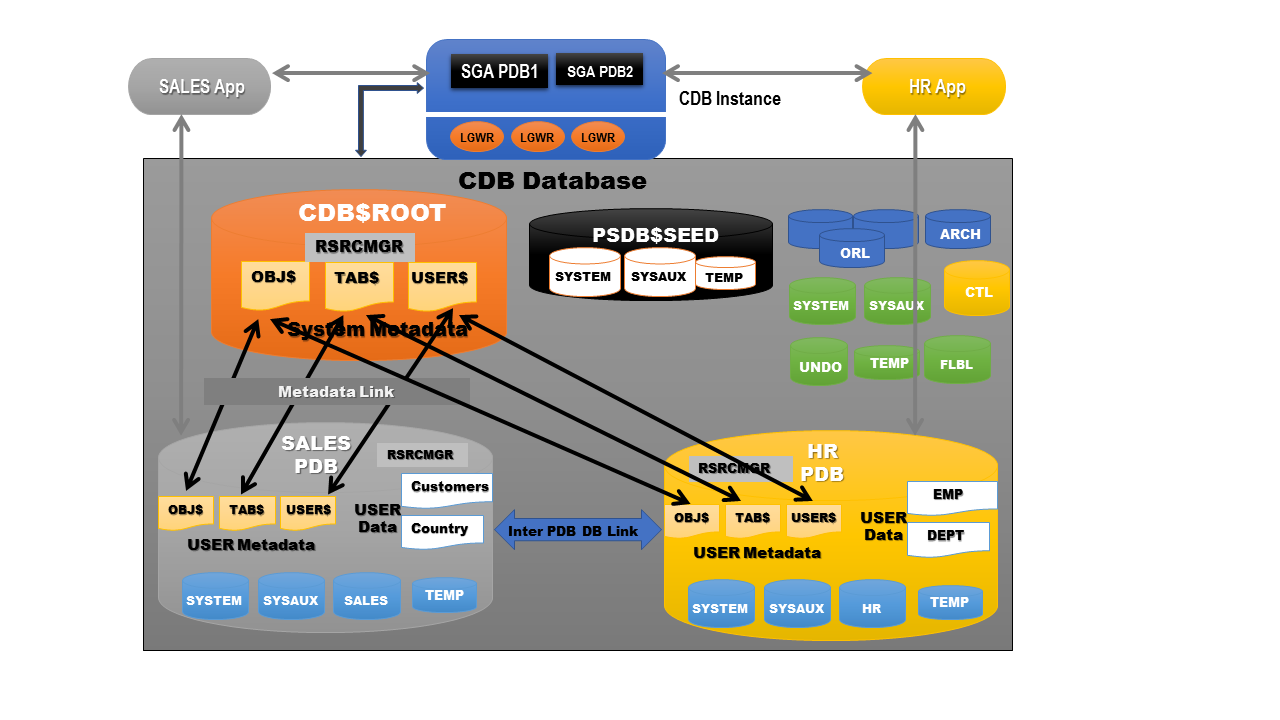
To understand the 19c upgrade process, first we need to understand the basics of EBS database portfolio – shown in the Figure 2: Database Portfolio Basics and Figure 3: Pluggable Database
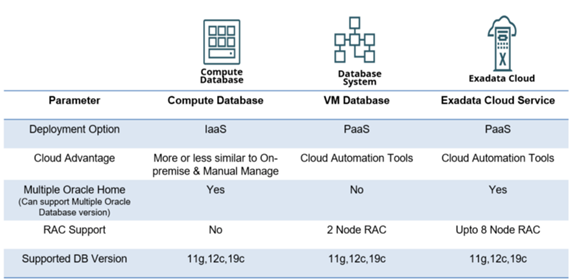
Figure 2: Database Portfolio Basics
Key Highlights of Upgrading to 19c:
- Oracle EBS supports single container database (CDB) with a single pluggable database (PDB)
- Any database version below 12c is considered a non-CDB database and 11g is a non-CDB database
- CDB databases are available for Cloud 12c and onward
- 19c database requires OEL 7
- Cloud databases hold structure as GRID Home and database Home
Figures 4 and 5 (from left to right): Oracle Grid Home and Database Home
Upgrading the Database on OCI
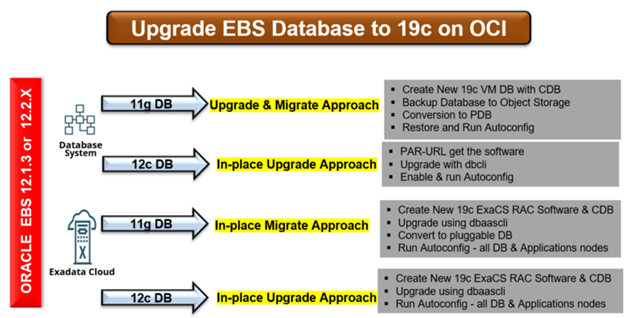
There are various approaches for upgrading the database, including migrating, and upgrading or performing an “in-place” upgrade, as shown in the diagram below:
Figure 6: Performing an In-Place Upgrade
For a non-CDB database, an additional step is required to convert the database into a PDB. This is done by creating a descriptor file and restarting the database. Additionally, as depicted in the diagram above, a virtual machine database with a 12c database requires an in-place upgrade and a PAR-URL for Oracle software.